Knowing the difference between centripetal force and centrifugal force is important in understanding the motion of objects along curved trajectories. These forces do not only explain natural phenomena but also are a key concept in designing advanced technologies.
Table of Contents
Introduction
In physics, objects moving along curved paths are subject to forces that determine their motion.
Among these forces, centripetal force is a real force that acts toward the centre of the curve. It ensures that the object maintains its circular path. In contrast, centrifugal force is a pseudo-force (perceived in a rotating frame of reference). It gives the illusion of being pushed outward from the centre of the curve.
While centripetal force is essential for real-world applications like road design, centrifugal force is crucial for analysing systems in non-inertial frames, such as spinning machines and rotating spacecraft. These forces provide insights into diverse phenomena ranging from planetary orbits to mechanical operations.
What is Centripetal Force?
Centripetal force is the force that is required to make an object follow a circular path.
It acts perpendicular to the velocity of the object and always points toward the centre of the circular path. Without centripetal force, as per Newton’s first law of motion, the object would move in a straight line due to inertia.
Mathematical Formulation
The centripetal force is given by the equation:
![]()
Here,
 = centripetal force
= centripetal force = mass of the object
= mass of the object = tangential velocity of the object
= tangential velocity of the object = radius of the circular path
= radius of the circular path
How Does It Arise?
Centripetal force is not a force by itself. It arises due to various physical interactions. These interactions are of the following types:
- Tension
- Friction
- Gravitational Pull
- Electromagnetic Forces
What is Centrifugal Force
It acts outward, away from the centre of rotation, and arises due to the inertia of the object resisting the change in direction.
Note that, it is not a real force but rather a manifestation of the tendency of an object to continue its motion in a straight line. Thus, centrifugal force is a perceived or apparent force experienced by an observer in a rotating (non-inertial) frame of reference.
Mathematical Formulation
Mathematically, centrifugal force is represented by:
![]()
Here,
 = centripetal force
= centripetal force = mass of the object
= mass of the object = tangential velocity of the object
= tangential velocity of the object = radius of the circular path
= radius of the circular path
Why the Negative Sign?
The negative sign indicates that the force is an inertial effect rather than a real interaction that opposes the centripetal force (or frictional force, tension, etc.).
How Does It Arise?
Centrifugal force emerges in non-inertial frames as a consequence of inertia.
Why Centrifugal Force Matters?
The role of centrifugal force cannot be denied as it is a vital constituent of our natural world.
1. Rotating Frames of Reference
Centrifugal force simplifies the analysis of motion in non-inertial frames, such as rotating merry-go-rounds, carousels, or centrifuges.
2. Space Applications
Artificial gravity in space stations is created by rotating sections of the station, where centrifugal force simulates the effect of gravity.
3. Engineering and Daily Life
From washing machine dryers to cream separators, centrifugal force plays a critical role in the functioning of numerous devices.
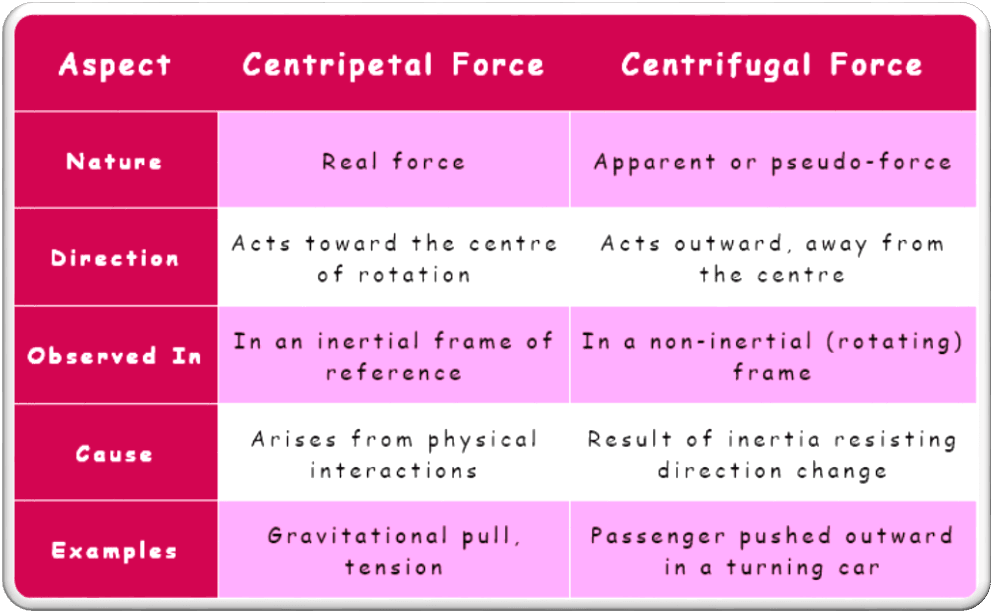
Differences between Centripetal Force and Centrifugal Force
Both these forces act as an action and reaction pair and thus align with the newton’s 3rd law of motion. The key differences between them are shown below.
Daily Life Applications of Centripetal Force and Centrifugal Force
1. Banking of Roads
Banking of roads refers to the inclined design of roads at curves, which enhances vehicle stability and safety.
How Does It Work?
The normal force on the banked surface provides a component that is directed toward the center of the curve and is referred to as centripetal force. This reduces reliance on friction and allows vehicles to turn safely, even at higher speeds.
The smooth turn is all thanks to the frictional force as well as the component of the normal force acting towards the centre of the curved path.
2. Washing Machine Dryer
The dryer section of a washing machine, a common household utility, removes water from clothes by spinning them at high speeds.
How Does It Work?
As the drum spins, centrifugal force pushes water outward through perforations in the drum. Meanwhile, centripetal force keeps the clothes confined within the drum, ensuring efficient drying.
3. Cream Separator
A cream separator is a device used to separate cream from milk by spinning the mixture.
How Does It Work?
During rotation, centrifugal force pushes the denser milk outward, while the lighter cream collects at the centre. This process is widely used in rural areas and dairy industries to process milk.
Conclusion
Centripetal force and centrifugal force are essential for understanding circular motion.
While centripetal force keeps objects on curved paths, centrifugal force provides a useful framework for analysing rotating systems.
Their applications, from road safety to industrial processes, demonstrate the profound impact of these forces on science and technology.
By mastering these concepts, we gain a deeper appreciation of the principles governing motion in the physical world.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
What is centripetal force?
Centripetal force is the real force acting toward the centre of a circular path, ensuring an object maintains its curved trajectory.
What is centrifugal force?
Centrifugal force is an apparent or pseudo-force perceived in a rotating frame of reference, acting outward from the centre of rotation.
What is the difference between centripetal force and centrifugal force?
Centripetal force is a real force that pulls an object toward the centre, while centrifugal force is an inertial effect experienced in a non-inertial frame, appearing to push outward.
What causes centripetal force?
Centripetal force arises due to interactions like tension, friction, gravitational pull, or electromagnetic forces, depending on the system.
Why is centrifugal force important?
Centrifugal force is essential for understanding motion in non-inertial frames and is used in practical applications like centrifuges, washing machines, and artificial gravity in space stations.
How do centripetal and centrifugal forces apply to road banking?
The banking of roads uses the centripetal force provided by the normal force and friction to help vehicles turn safely on curves. Centrifugal force must be considered to ensure stability.
How do these forces operate in a washing machine?
In a washing machine dryer, centrifugal force pushes water outward through the drum perforations, while centripetal force keeps the clothes inside, ensuring efficient drying.
What is the role of these forces in cream separators?
In cream separators, centrifugal force pushes the denser milk outward, while lighter cream collects at the centre, effectively separating the two substances.
