Energy and its classification in physics are an essential and fundamental concept. Energy can be classified either based on its form or the source it originates from.
Table of Contents
Introduction
Energy is a fundamental concept in physics that plays a crucial role in understanding the mechanics of the universe.
Whether it is the motion of planets, the functioning of machines, or the biological processes within living organisms, energy is always involved. From the heat in a stove to the warmth of a person’s body and the radiant energy of the sun, it is found in every aspect of our daily lives.
What is Energy?
Energy can be defined as,
“the capacity of a body to do work.”
Key Characteristics of Energy
Since energy is the ability to do work, so, it shares the key characteristics with the work.
Representation
Energy is represented by the symbol ![]() .
.
Unit
The SI unit of energy is the joule (![]() ), also called
), also called ![]() or
or ![]() .
.
Type of Quantity
Energy is a derived physical quantity.
Nature of Quantity
Energy is a scalar quantity, meaning it requires only magnitude and no direction.
Energy and Its Classification
Energy can be classified either based on either type or form. The terms “types of energy”, and “forms of energy” are often used interchangeably, but based on the context they have a delicate difference.
7 Forms of Energy
Forms of energy refer to the different ways in which energy exists or manifests in the physical world. It includes fundamental categories of energy based on physics.
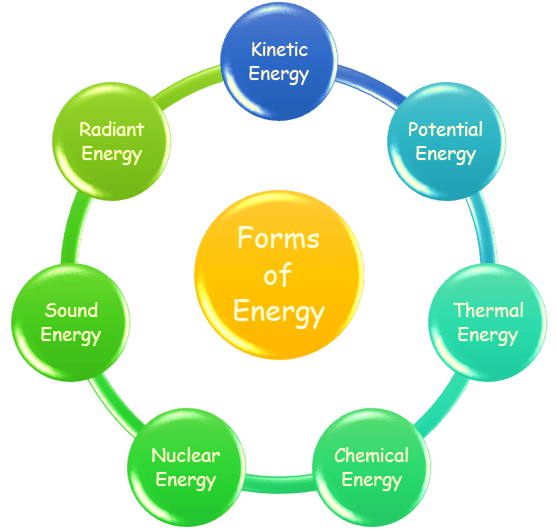
- Kinetic Energy
Kinetic energy is the energy of a moving object due to its motion. It depends on the mass and speed of the object. The faster or heavier an object is, the more kinetic energy it has.
- Potential Energy
Potential energy is stored energy based on the position or condition of an object. It can be due to height, stretch, or electric charges. This energy has the potential to do work when the position or condition changes.
- Thermal Energy
Thermal energy is the energy related to the temperature of a substance. It comes from the motion of particles within the object. The faster the particles move, the more thermal energy and heat it has.
- Chemical Energy
Chemical energy is stored in the bonds of atoms and molecules. It is released or absorbed during chemical reactions. Fuels and food are common sources of chemical energy.
- Nuclear Energy
Nuclear energy comes from reactions in the nucleus of atoms. It is released through processes like fission or fusion. This energy powers nuclear plants and the sun.
- Sound Energy
Sound energy is carried by vibrations traveling through a medium like air, water, or solids. It is produced when an object vibrates. These vibrations create sound waves that our ears can detect.
- Radiant Energy
Radiant energy is carried by light and other electromagnetic waves. It travels through space and does not need a medium. The sun is a major source of radiant energy.
2 Types of Energy Resources
There is a broader classification that includes both forms of energy and their sources or categories. It refers to how energy is used or transformed.
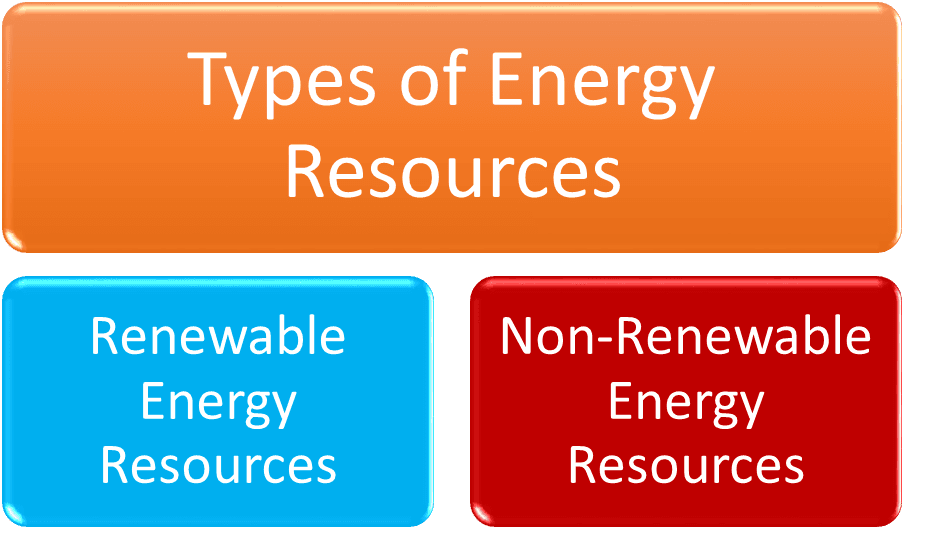
- Renewable Energy
Energy from sources that replenish itself naturally is called renewable resources. For instance, solar, wind, hydro.
- Non-renewable Energy
Energy from sources that are finite and cannot replenish itself naturally. For instance, coal, oil, and natural gas.
Conclusion
From everyday occurrences to advanced technological applications, energy transformations play a crucial role in shaping the physical world. By studying these concepts, we can optimise energy usage, improve efficiency, and develop sustainable solutions for the future.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
What is energy and its classification in physics?
Energy is the capacity of a body to do work. It is a fundamental concept that explains various physical and chemical processes. Its classification is based on the form of energy and the source it is obtained from.
What is the SI unit of energy?
The SI unit of energy is the joule (J), which is equivalent to Nm.
What are the main forms of energy?
The seven primary forms of energy are kinetic, potential, thermal, chemical, nuclear, sound, and radiant energy.
How is kinetic energy different from potential energy?
- Kinetic Energy is the energy of motion
 .
. - Potential Energy is stored energy due to position or configuration
 .
.
What is the difference between renewable and non-renewable energy?
- Renewable energy comes from sources that replenish naturally (e.g., solar, wind, hydro).
- Non-renewable energy comes from finite resources (e.g., coal, oil, natural gas).
Why energy is considered a scalar quantity?
Energy has only magnitude and no direction, making it a scalar quantity.
How is thermal energy different from chemical energy?
- Thermal energy is related to heat and temperature.
- Chemical energy is stored in chemical bonds and released during reactions.
What is nuclear energy and how is it generated?
Nuclear energy is released from atomic nuclei through fission (splitting of atoms) or fusion (combining of atoms), commonly used in power plants and the sun.
How does sound energy travel?
Sound energy travels in the form of waves through a medium (solid, liquid, or gas) but cannot travel through a vacuum.
Why is the study of energy important?
Understanding energy helps optimise its usage, improve efficiency, and develop sustainable solutions for industries, transportation, and daily life.
