What is work-energy principle? The Work-Energy Principle and Conservation of Energy are some of the fundamental principles governing energy transformation.
Table of Contents
Introduction
Energy, along with matter, forms the foundation of our universe. Understanding how energy operates and interacts with objects is crucial for various scientific and engineering applications.
One of the most important principles related to energy in classical mechanics is the Work-Energy Principle, which establishes a relationship between the work done on an object and its kinetic energy. This relationship aligns with the law of conservation of energy.
What is Energy?
Energy can be defined as,
“the ability of a body to do work.”
What is Work Done?
In physics, work done is defined as,
“product of force and distance moved in the direction of force.”
What is Work-Energy Principle?
The Work-Energy Principle states that;
“the work done on an object by external forces equals the change in its kinetic energy.”
Mathematical Formulation
Consider a car moving with a changing speed from A to B as shown.
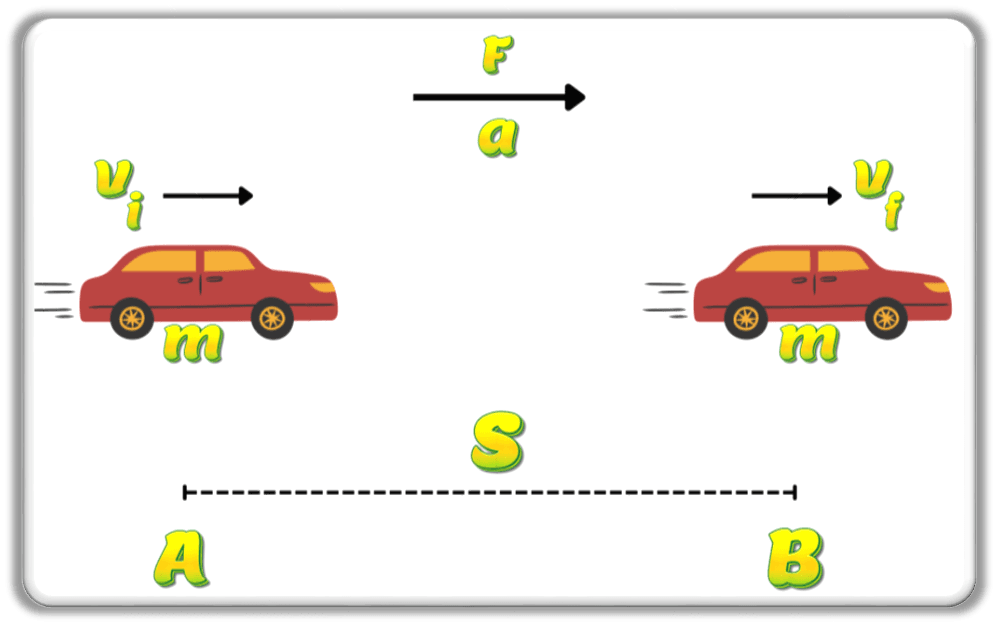
Here,
![]() distance
distance
![]() final speed
final speed
![]() initial speed
initial speed
![]() acceleration
acceleration
![]() force
force
![]() work done
work done
![]() final kinetic energy
final kinetic energy
![]() initial kinetic energy
initial kinetic energy
Now, applying the Newton’s 3rd equation of motion,
![]()
From the definition of force.
![]()
![]()
The 3rd equation can be rewritten as follows,
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
Inference
This principle helps in analysing motion, solving problems in mechanics, and understanding energy transformations.
Applications of the Work-Energy Principle
- Automobiles
Braking a car decreases its kinetic energy through negative work done by friction.
- Roller Coasters
The potential energy at the highest point converts into kinetic energy as the coaster moves downward.
- Sports
When a football is kicked, the work done by the player’s foot increases its kinetic energy.
- Construction
Lifting materials to a certain height increases their potential energy, which later converts into kinetic energy when released.
- Space Science
In space applications, it is used in launching and manoeuvring spacecraft by understanding energy transformations.
- Safety Mechanisms
It helps design airbags and crumple zones in vehicles to reduce impact forces.
Work-Energy Principle and Conservation of Energy
The Work-Energy Principle is related to the Law of Conservation of Energy, which states that;
“energy can neither be created nor be destroyed but only transformed from one form to another.”
Mathematical Formulation
![]()
OR
![]()
OR
![]()
OR
![]()
In an ideal system with no non-conservative forces (like friction), the total mechanical energy – the sum of kinetic energy (K.E.) and potential energy (P.E.) – remains constant.
However, in real-world scenarios, some energy is lost as heat or sound due to non-conservative forces.
Conclusion
Though a classical concept, understanding energy and the Work-Energy Principle is fundamental to physics and engineering.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
What is Work-Energy Principle?
The Work-Energy Principle states that the work done on an object by external forces is equal to the change in its kinetic energy.
How is work related to energy?
Work is the transfer of energy. When work is done on an object, its energy changes, either in the form of kinetic or potential energy.
What is the Law of Conservation of Energy?
The Law of Conservation of Energy states that energy cannot be created or destroyed; it can only transform from one form to another.
How is the Work-Energy Principle applied in daily life?
It is used in automobiles (braking and acceleration), roller coasters, sports, construction, space science, and safety mechanisms like airbags.
What is the mathematical expression for the Work-Energy Principle?
![]()
where ![]() is the work done,
is the work done, ![]() is mass, and
is mass, and ![]() and
and ![]() are the final and initial velocities, respectively.
are the final and initial velocities, respectively.
Can energy be destroyed?
No, according to the Law of Conservation of Energy, energy can only change forms but is never destroyed.
What happens when friction is present?
In real-world situations, friction converts mechanical energy into heat, causing some energy loss. However, the total energy (including heat) remains conserved.
How does a roller coaster demonstrate the Work-Energy Principle?
A roller coaster converts potential energy at the highest point into kinetic energy as it moves downward, following the conservation of energy.
What is the difference between kinetic and potential energy?
Kinetic Energy (K.E.) is the energy of motion ![]() .
.
Potential Energy (P.E.) is stored energy due to position ![]() .
.
Why is the Work-Energy Principle important in engineering?
It helps engineers design efficient machines, vehicles, and safety mechanisms by understanding how energy is transferred and transformed.
