Understanding the 8 key differences of elements vs compounds vs mixtures is vital to easily identify and distinguish all types of substances around you!
Table of Contents
Introduction
Previously, we discussed element, compound, and mixture separately and gained an in-depth understanding of how everything around us is made of. Whether it is the air you breathe, the water you drink, or the gold in your jewellery—everything is made up of pure substances (element and compound), or impure substances (mixture).
Understanding the difference between these three types of matter is a big step in learning about chemistry. Here, we shall do a comparative study of these types of matter.
What Are They?
Before we dive into a comparison table, here is a quick recap.
Element
It is the simplest form of the matter. It is made of only one type of atom. For instance, gold, oxygen, helium, etc.
Compound
It is formed by a chemical combination of two or more different elements in a fixed ratio. Like water (H₂O) or table salt (NaCl).
Mixture
A physical blend of two or more substances. These are not chemically bonded—like a fruit salad or salt water.

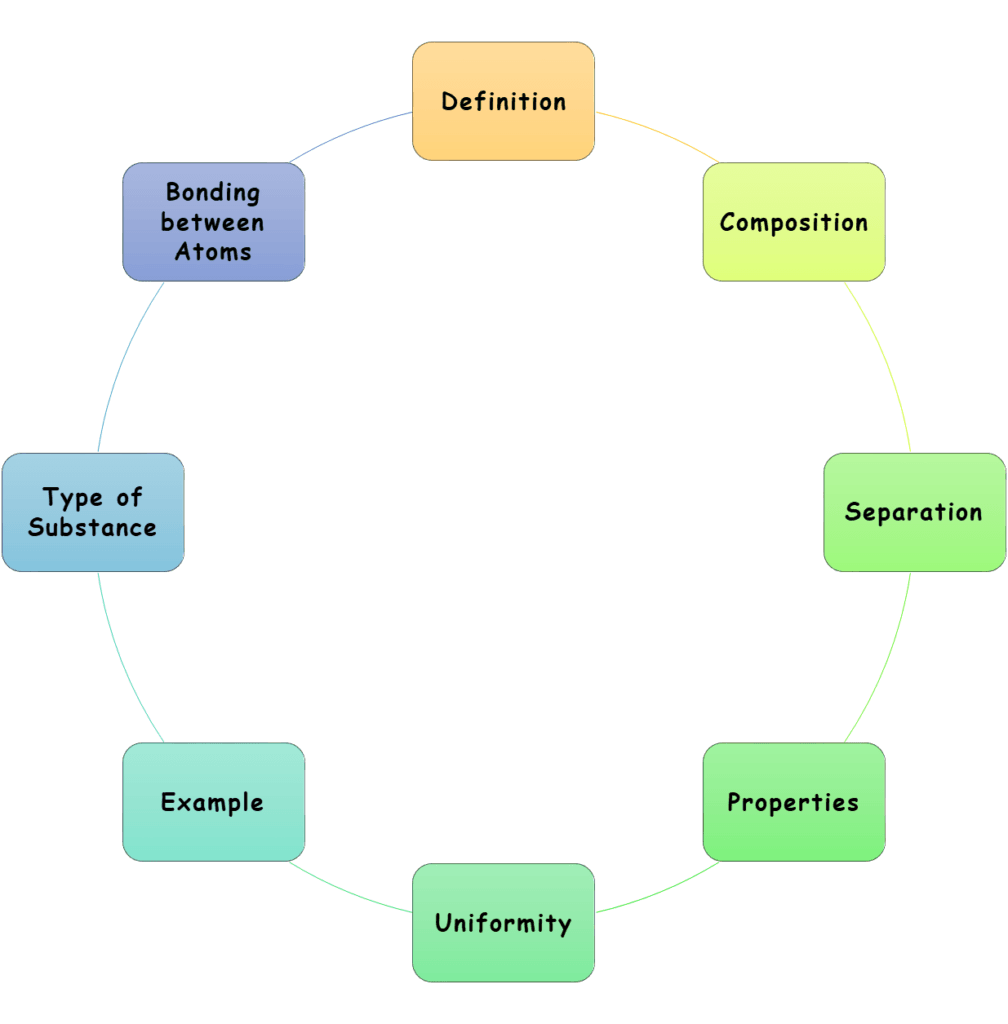
8 Differences between Element, Compound, and Mixture
Here is a simple and easy-to-understand comparison between them.
1. Definition
| Substance | Definition |
| Element | A pure substance made of only one kind of atom. |
| Compound | A chemically combined pure substance, formed by two or more different elements. |
| Mixture | A combination of two or more substances that are not chemically bonded. |
2. Composition
| Substance | Composition |
| Element | Contains only one type of atom. |
| Compound | Atoms of different elements in a fixed ratio. |
| Mixture | Different substances are mixed physically. |
3. Separation
| Substance | How It Can Be Separated |
| Element | Cannot be broken down by normal chemical methods. |
| Compound | Can be broken into elements by chemical methods (e.g., electrolysis). |
| Mixture | Can be separated by physical methods (like filtration or evaporation). |
4. Properties
| Substance | Properties |
| Element | Unique to the individual element (e.g., colour, density, reactivity). |
| Compound | Very different from the element(s) they are made of. |
| Mixture | Similar to the properties of the substances that make them up. |
5. Uniformity
| Substance | Uniformity |
| Element | Always uniform (same throughout) behaviour. |
| Compound | Always uniform (same throughout) behaviour. |
| Mixture | Can be homogeneous (uniform) or heterogeneous (not uniform). |
6. Examples
| Substance | Examples |
| Element | Gold (Au), Oxygen (O₂), Iron (Fe), Helium (He) |
| Compound | Water (H₂O), Carbon Dioxide (CO₂), Salt (NaCl), Ammonia (NH₃) |
| Mixture | Air, Salt water, Salad, Soil, Trail mix |
7. Type of Substance
| Substance | Type |
| Element | Pure substance |
| Compound | Pure substance |
| Mixture | Impure substance |
8. Bonding between Atoms
| Substance | Bonding |
| Element | No chemical bonding (just a single type of atom). |
| Compound | Atoms are chemically bonded together. |
| Mixture | No chemical bonds between the substances—they are just mixed. |
Quick Tips to Remember
- Element is like the letters of the alphabet – the main ingredient and the building blocks of matter.
- Compound is like words – combinations of elements with new meanings (properties).
- Mixture is like a sentence – all ingredients are still there and can be picked apart.
Try This at Home!
Grab a glass of salt water. Is it an element, compound, or mixture?
Well! It is a mixture!
Why?
Because the salt and water are not chemically bonded—they are just mixed physically.
Conclusion
Understanding the pure and impure substances makes the rest of chemistry a whole lot easier. It prepares you to identify the things around you.
Have questions or want to see more examples? Drop them in the comments! You can also visit here for an in-depth study of these three types of matter.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Write the differences of elements vs compounds vs mixtures.
Element
It is a pure substance made of only one type of atom and cannot be broken down by normal physical means or chemical means.
Compound
It is also a pure substance made of two or more elements chemically combined in fixed proportions. It can be broken down chemically.
Mixture
A combination of two or more substances is physically combined where components retain their properties and can be separated physically.
Can you identify a mixture, element, or compound out of the following? Milaf Cola, petroleum, sugar, table salt, blood, gun powder, urine, aluminium, silicon, tin, lime, and ice cream.
Milaf Cola: Mixture
Petroleum: Mixture
Sugar: Compound
Table salt: Compound
Blood: Mixture
Gun powder: Mixture
Urine: Mixture
Aluminium: Element
Silicon: Element
Tin: Element
Lime (calcium oxide): Compound
Ice cream: Mixture
Which one of the following can be separated by physical means? (a) mixture (b) element (c) compound
(a) Mixture
State three reasons why you think air is a mixture and water a compound.
Nature of Combination
Air contains various gases (like nitrogen, oxygen, and carbon dioxide) that are physically combined, whereas water is composed of hydrogen and oxygen chemically bonded in a fixed ratio.
Composition
The composition of air varies depending on location and environmental factors. In contrast, water (H₂O) has a fixed composition by mass — 2 parts hydrogen to 16 parts oxygen, or 1:8 by mass.
Separation of Components
The components of air can be separated by physical methods such as filtration, distillation, or fractional liquefaction, while the elements in water can only be separated by chemical methods such as electrolysis or thermal decomposition.
Explain why are hydrogen and oxygen considered elements whereas water is a compound.
- Hydrogen and oxygen consist of only one type of atom (elements).
- Water consists of hydrogen and oxygen chemically combined in a fixed ratio, forming a new substance (compound).
State the reasons: soft drink is a mixture and water is a compound.
- Soft drinks contain various substances (water, sugar, CO₂) physically mixed, not chemically bonded.
- Water is a compound and has chemically bonded hydrogen and oxygen atoms with a fixed composition.
Classify the following into elements, compounds, or mixtures:
i. He and H2
ii. CO and Co
iii. Water and milk
iv. Gold and brass
v. Iron and steel
i. He (element), H₂ (element – molecule of hydrogen)
ii. CO (compound), Co (element – cobalt)
iii. Water (compound), milk (mixture)
iv. Gold (element), brass (mixture/alloy)
v. Iron (element), steel (mixture/alloy)
State the nature and name of the substance formed by combining the following:
i. Zinc + Copper
ii. Water + Sugar
iii. Aluminium + Sulphur
iv. Iron + Chromium + Nickel
i. Zinc + Copper: Alloy (brass) – mixture
ii. Water + Sugar: Mixture (solution)
iii. Aluminium + Sulphur: Compound (aluminium sulphide)
iv. Iron + Chromium + Nickel: Alloy (stainless steel) – mixture
List five characteristics by which a compound can be distinguished from a mixture.
1. Compounds form new substances; mixtures do not.
2. Compounds have fixed composition; mixtures do not.
3. Compounds have chemical bonds; mixtures have physical combinations.
4. Compounds require chemical methods to separate; mixtures can be separated physically.
5. Compounds have different properties from their elements; mixtures retain properties of components.
Write the similarities between elements, compounds, and mixtures.
All are made up of matter.
All have mass and occupy space.
All can be found in solid, liquid, or gas states.
