In the era of technology, every individual must explore different types of computing systems such as computers, software systems, computer networks, and the Internet as per their interest.
Table of Contents
Introduction
Sarah, just 7 years old, was tapping away on her tablet when she suddenly looked up at her father.
“Baba,” she asked, eyes wide, “how does my tablet know what to do?”
A simple question — but behind it, a world of wonder. Her dad smiled.
“Well,” he began, “inside that little screen is a whole team of tiny helpers — not real people, but clever parts working together to follow instructions and make things happen.”
He continued explaining, from sending messages to shopping online, from watching cartoons to hearing your favourite song — every click, swipe, and tap is powered by a hidden world of tiny workers and invisible signals.
Welcome to the world of computing systems — where smartly designed parts, cleverly coded programs, and a spark of electricity come together to bring your digital world to life.
What Is a Computing System?
A computing system is a combination of hardware, software, and electricity working together to process data and perform tasks.
From a basic calculator to a global data centre, all computing systems follow this same foundational structure. These are artificial systems developed by humans for humans.
Core Components of a Computing System
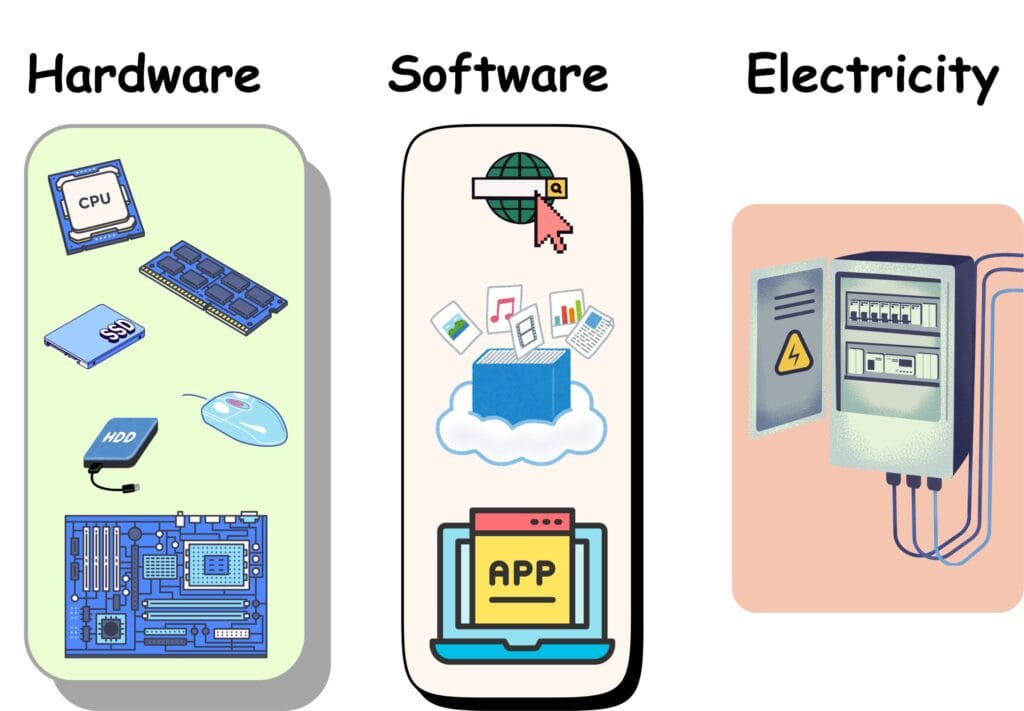
1. Hardware
These are the tangible components of any device. Think of them as the body of a computer. These include:
- CPU (Central Processing Unit) – The brain that processes information.
- RAM (Random Access Memory) – Temporary memory for active tasks.
- Storage – Where your files, apps, and data are saved.
- Input Devices – Like keyboards, mice, or cameras.
- Output Devices – Like monitors, printers, or speakers.
2. Software
Software is the instructions that tell the hardware what to do. It is like the soul of the computing system. Broadly, it is classified as:
- System Software – The operating system (Windows, macOS, Linux) that runs the computer.
- Application Software – Programs like web browsers (Google), games, or word processors (MS Word) that help users perform specific tasks.
3. Electricity
Electricity is the power source, fuelling the whole system. It energises all the hardware and lets the software come alive.
No Power = No Computing
Types of Computing Systems
Computing systems come in many shapes and sizes. Here are some examples:
- Personal Computers & Mobile Devices – Laptops, phones, tablets.
- Software Systems – Apps, Software, online platforms, or tools used daily.
- Computer Networks – Groups of systems connected to share information.
- The Internet – The largest network on Earth, connecting billions of devices.
Computer Networks
A computer network is a group of devices connected to share resources.
- The connection between them can be physical (like cables) or non-physical (like Wi-Fi).
- Shared resources can include files, printers, or internet access.
Why Networks Matter | Objectives
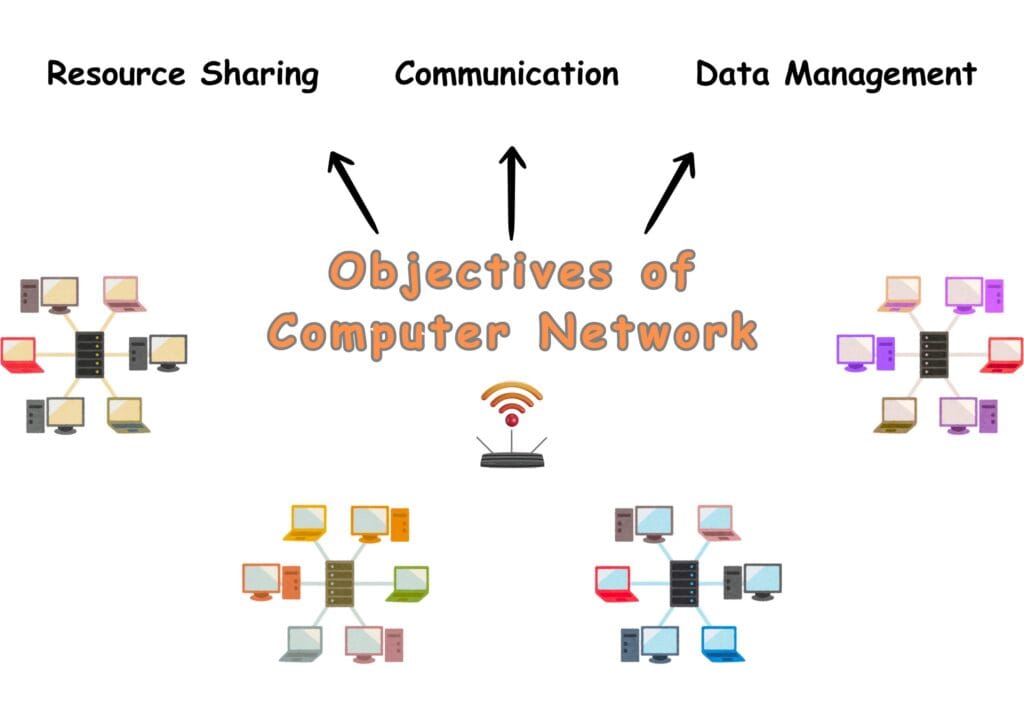
- Resource Sharing
For example, share data, printers, or apps within or outside the organisation.
- Communication
For instance, transfer of emails, chats, and audio or video calls between users.
- Data Management
For instance, teams work together on shared documents to collaborate.
Key Network Components
i. Hardware
- Router
Sends data between different networks (e.g., from your home network to the internet).
- Switch
Connects devices within the same network, like computers in a local office.
- Network Cables
Transfer data physically in wired setups (e.g., Ethernet, fibre optic cables).
ii. Software
- Protocols
These are rules that govern digital communication (e.g., TCP/IP).
- Network Operating Systems
These systems manage and control network resources (e.g., Windows Server, Linux).
Environment of a Network System
Computer networks operate in various environments, often via the Internet. Common environments include:
- Data centres
- Office buildings
- Global operations (international or remote teams)
These environments are strongly influenced by factors such as network design, security, and performance.
Types of Networks
LAN (Local Area Network)
- It connects devices within a limited area.
- For example, homes, schools, or offices.
WAN (Wide Area Network)
- It spans large geographic areas like cities, countries, or even continents.
- The Internet is the largest and most well-known example of a WAN.
MAN (Metropolitan Area Network)
- It is sandwiched between LAN and WAN. It covers a larger area than a LAN but smaller than a WAN.
- It, typically, covers a city or large campus and is often used by government, universities, or large companies with buildings spread across a city.
The Internet
The Internet (traditionally written with capital ‘I’) is “A Network of Networks.”
It is a massive global network connecting billions of devices (laptops, mobiles, printers, etc.). It enables communication, data sharing, and access to services worldwide.

Common Internet Protocols
- TCP/IP
Transmission Control Protocol / Internet Protocol is a core protocol for reliable communication and data transfer.
- UDP
A User Datagram Protocol that is faster but less reliable. It is used for streaming or gaming.
- FTP
File Transfer Protocol is responsible for transferring files between systems (e.g., a USB).
- POP
The Post office Protocol retrieves emails from servers.
Interaction among Components
Consider a real-world example like visiting a website.
1. You type a web address into your browser (Google or Safari etc.).
2. The browser sends a request over the internet using TCP/IP.
3. A web server receives it and sends back the content.
4. The page appears on your screen — all in seconds!
Environment of the Internet
Now the question is, “Where does the Internet Operate?” The internet connects devices at:
- Homes
- Data Centres
- Mobile Networks
- Schools and Offices
Each environment affects speed, design, and security.
Conclusion
In this blog, we explored three key ideas:
- A computing system includes hardware, software, and electricity.
- Computer networks connect devices to share resources and enable communication.
- The Internet is the largest computing system, linking people and machines around the world. Protocols like TCP/IP ensure everything runs smoothly behind the scenes.
Understanding how computing systems work can help you:
- Stay safer online
- Prepare for tech-related careers
- Use technology more effectively
- Solve and troubleshoot problems more confidently
Whether you are a student, a professional, or just someone curious about technology, understanding the digital world benefits everyone.
The world of computing is vast and constantly evolving. By starting with the basics, you’re building a strong foundation for exploring deeper topics like:
- Cybersecurity
- Cloud Computing
- Artificial Intelligence
So stay curious — and keep exploring the systems that power our digital lives.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Why does it matter to explore different types of computing systems?
Exploring different types of computing systems is beneficial because it helps to understand:
- How do digital tools work?
- How you can use them more efficiently and securely?
- How do they interact with each other and the environment?
This knowledge empowers you in the following domains:
- to solve problems
- to make informed tech decisions
- to prepare for careers in the technology-driven world
What are the three main requirements for a computing system to function?
A functioning computing system requires:
- Hardware – the physical components like CPU, memory, and input/output devices.
- Software – programs that give instructions to the hardware.
- Electricity – the power that enables hardware and software to operate together.
What is the difference between computing systems such as computers, software systems, computer networks, and the Internet?
- Computers are physical devices that process data.
- Software Systems are the programs and apps that run on computers to perform tasks.
- Computer Networks connect multiple devices to share resources and data.
- The Internet is the largest network in the world that connects billions of computing systems globally.
What is the role of a CPU in a computing system?
The CPU (Central Processing Unit) acts as the brain of a computer. It processes instructions and controls how other parts of the computer work together.
What is the difference between RAM and storage?
RAM (Random Access Memory) temporarily stores data for active tasks. It makes your device fast and responsive.
Storage (like hard drives or SSDs) holds files, apps, and data permanently until deleted.
Why are protocols important in networking?
Protocols are standardised rules that allow computers to communicate with each other. Without them, devices would not understand what to do or share data properly.
How does Wi-Fi differ from Ethernet in a network?
Wi-Fi is a wireless method of connecting devices to a network. It is more flexible.
Ethernet uses physical cables. It often provides faster and more stable connections.
Can mobile phones be considered computing systems?
Yes!
Mobile phones are advanced computing systems. They include hardware (touchscreen, processor), software (apps and OS), and use electricity (battery) to perform tasks.
What is an example of application software?
Application software helps users to complete specific tasks on a device. For example:
- Mobile Games
- Google Chrome
- Microsoft Word
How does understanding computing systems help with cybersecurity?
When you understand how systems work, you are a better-equipped soldier. You can recognise suspicious activity, protect personal data, and safely use online services.
It is essential for staying secure in the digital world.
