Basics of digital systems is the foundational in the information age. They involve clear, distinct steps (0s and 1s) instead of smooth, continuous waves.
Table of Contents
Introduction
Digital systems are the hidden force behind the modern world. From smartphones and laptops to smartwatches and even cars — they are everywhere. But what does the word “digital” really mean? And why is it such a big deal?
The word “digital” comes from the Latin word digitus, meaning finger. In modern terms, digital refers to information that is represented using discrete values, usually just 0 and 1, called bits. So when we say something is digital, we mean it works by processing, storing, or transmitting information in bits.

Digital is not just a buzzword.
Digital = Binary = Better Control, Better Quality, and Smarter Tech
What Is a Digital System?
A digital system is any system that represents and processes information using binary — just 0s and 1s, like OFF and ON signals.
By putting many bits together, digital systems can:
- Control machines
- Send messages
- Guide rockets
- Store songs
- Play games
Examples
Some of the digital devices used in our daily lives are:
- Laptops
- Smart TVs
- Calculators
- Smartphones
- Digital watches
- Smart home devices
All of these devices work by handling millions (or even billions) of 0s and 1s every second.
What is a Signal?
A signal is a way to carry or represent information.
OR
A signal is like a messenger that carries a message (data) from one point to another.
OR
A signal is a form of energy that varies over time and can be used to communicate, control, or transfer data from one place to another.
Before diving deeper into how digital systems work, we need to understand how information is carried through signals.
Types of Signals
There are two main types of signals:
- Analog Signals (also spelled analogue)
- Digital Signals

Difference between Analogue Signals vs Digital Signals
A comparison between an analogue signal and a digital signal is given here.
| Feature | Analog Signals | Digital Signals |
| Nature | Continuous, smooth changes | Discrete, jumps between set values (0 and 1) |
| Examples | Human voice, music, temperature, light | Computer data, text messages, digital audio |
| Appearance | Looks like a flowing wave (curved line) | Looks like a staircase (blocky, with clear steps) |
| Accuracy | Can lose quality and get distorted easily over time | Maintains quality over time, even after many copies |
| Application | Radios, microphones, vinyl records | Computers, phones, CDs, digital TVs |
| Analogy | Imagine a dimmer light switch (smoothly changes brightness) | Imagine a regular light switch (either fully ON or fully OFF) |
Why Do We Need Both?
The real world is analogue, as all the events occur (changes) smoothly, like sounds, light, heat, etc. But computers only understand digital, meaning the language of binary (0s and 1s). So, there is a need to convert between the two:
Analog to Digital Converter (ADC) ⇌ Digital to Analog Converter (DAC)
A Comparison of ADC and DAC
| Analog to Digital Converter (ADC) | Digital to Analog Converter (DAC) |
| Takes real-world input (like your voice) and turns it into digital data. | Takes digital data and turns it back into something you can hear or see. |
| Think of it like recording your voice as a bunch of tiny numbers. | Like playing your recorded voice back through a speaker. |
Example
To understand how ADC and DAC work together, let’s walk through what happens when you speak in a microphone:
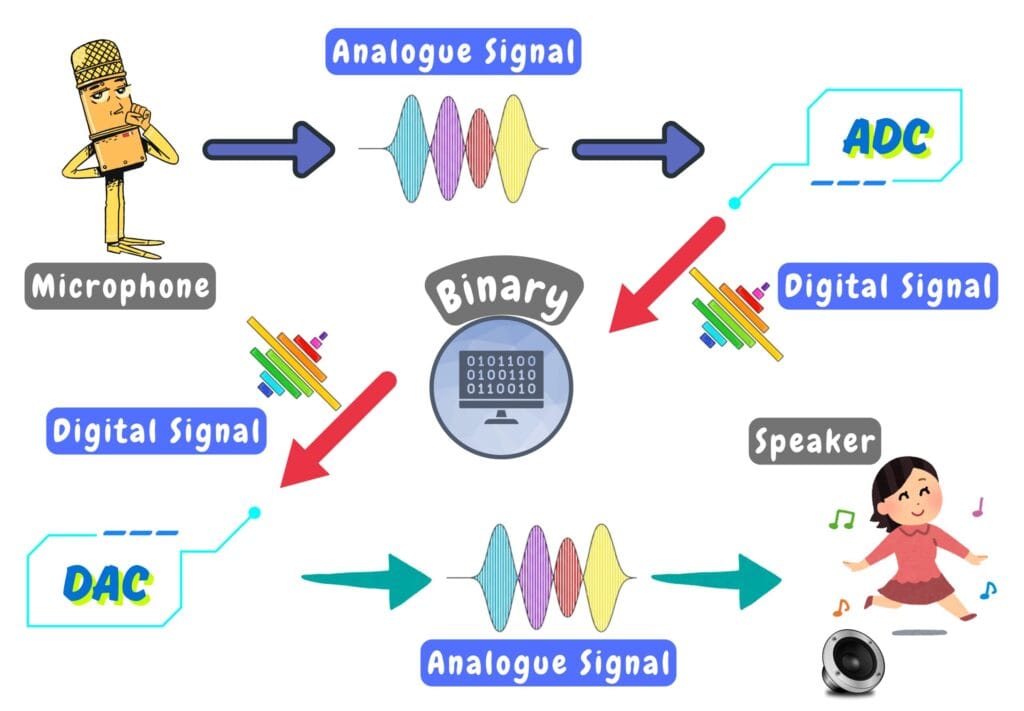
1. You speak into the phone.
Your voice is an analogue signal — a smooth, continuous sound wave.
2. The phone captures your voice (ADC).
An Analog-to-Digital Converter (ADC) inside the phone converts your voice into digital data — 0s and 1s.
3. The digital signal is sent.
Your voice, now in digital form, travels quickly and clearly over the network (wired network, Wi-Fi, mobile data, etc.), with minimal loss or distortion.
4. The speaker receives the digital signal (DAC).
A Digital-to-Analog Converter (DAC) converts the digital data back into an analogue signal.
5. The speaker plays the sound.
The speaker turns the analogue signal into sound waves, and the person on the other end hears your voice.
This real-world example shows how analogue and digital systems work together to let us communicate easily across the world.
Why Go Digital?
Digital technology has taken over almost every domain of our lives. It solves some of the biggest problems in communication, data processing, and storage. The key motives for setting foot into the digital world are:
1. Less Noise, More Clarity
Analog signals degrade over time and distance. For instance, think of static on an old radio.
Digital signals, on the other hand, are much more resistant to noise, because they only need to distinguish between two states — 0 and 1. That makes them cleaner and more reliable.
2. Easier to Store, Copy, and Share
With analogue data, each copy gets worse. For instance, an old cassette tape in your grandfather’s collection.
Alternatively, with digital data, you can make perfect copies, store them in tiny chips or huge servers, and share them instantly.
3. Faster and Smarter Processing
Digital devices process billions of calculations per second using logical operations on binary data. For instance, your phone and/or a supercomputer.
This speed and precision are the key to everything from real-time video editing to AI and machine learning.
4. Empowers Modern Life
Your whole life in the current world is built on digital systems. For instance, every app, website, GPS, streaming service, video call, etc.
Without digital technology, the modern world simply would be a fantasy.
A Glimpse of Digital Logic
Once information is in digital form, devices use logic circuits to make decisions and perform tasks. You can learn about them once available here.
Just remember, these circuits are made of tiny building blocks called logic gates. For instance:
- AND
- OR
- NOT
These are basic operations that work on bits. Combined together, they can do math, control robots, or run apps. They are just like LEGO bricks; you can build anything using these logic pieces.
Conclusion
Digital systems are invisible ninjas of the modern world. They run almost everything we use today. From simple bits to smart devices, they turn real-world signals into something computers can understand — and back again.
Understanding how signals become logic gives you a BTS (behind-the-scenes) look at the digital world. It may spark your interest in building the tech of the future.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
What are the basics of digital systems, and how do they work?
Digital systems use 0s and 1s (binary) to process and store information. They power devices like phones, computers, and smart gadgets through logic circuits and digital signals.
What is the difference between analogue signals vs digital signals?
Analogue signals are continuous (like sound), while digital signals are made of steps (0s and 1s). Digital is more reliable and easier to store and share.
Why are digital systems used in modern electronic devices?
Digital systems are faster, more accurate, and less affected by noise — ideal for modern tech like smartphones, laptops, and smart TVs.
How do digital devices convert analogue signals into digital form?
They use ADCs (Analog-to-Digital Converters) to turn real-world inputs like voice into digital data that computers can understand.
Can digital signals replace analogue signals completely?
Not fully — the real world is analogue. But digital tech uses converters (ADC/DAC) to work with both types effectively.
What are real-world examples of digital systems in everyday life?
Smartphones, calculators, digital watches, and smart TVs — all use digital systems to function.
Why do digital signals maintain quality better than analogue signals?
Digital signals do not degrade like analogue ones. They are cleaner, clearer, and easier to copy without losing quality.
How does a mobile phone use both digital and analogue systems?
Phones convert your analogue voice to digital to send, then back to analogue so the other person can hear you.
What are logic gates, and how do they power digital systems?
Logic gates like AND, OR, and NOT control how digital systems make decisions using 0s and 1s.
How are digital systems transforming industries and daily living?
They enable smart homes, fast communication, digital payments, and AI — making life easier and more connected.