Knowing the force in Physics and its 4 effects is an essential concept. Whether it is the mechanics of daily life or the orbiting celestial bodies, force shapes our world, the way we know it.
Table of Contents
Introduction
Force is a fundamental aspect of physics. In the universe, it is a prominent agent in every action and reaction. The understanding of force has evolved over centuries. It forms the backbone of classical mechanics and modern physics.
Here, we will discuss important aspects of force in physics and its 4 effects, along with the critical role they play in shaping our understanding of the natural world.
Historical Background
The concept of force has evolved.
Ancient Philosophy
In ancient times, motion and force used to be seen through a qualitative lens. For instance, philosopher Aristotle believed that a constant force was necessary to maintain motion. His idea about the force persisted for centuries.
Medieval Period
During the medieval period, Islamic scholars like ibn Bajjah (Avempace), Abu’l-Barakat al-Baghdadi, Ibn Sina (Avicenna), and Ibn al-Haytham (Alhazen) made significant contributions to understanding motion and force.
They worked on the concept of mayl (inclination) and hinted at what we now recognize as momentum and inertia.
While these Islamic scholars did not develop a modern concept of force as we understand it today, their work laid the foundation for later advancements.
Their critical analysis of Aristotelian physics and their innovative ideas about the nature of motion and force contributed to the development of scientific thought and paved the way for the scientific revolution.
Classical Period
The classical era saw the first true revolution in the understanding of force. Thanks to Galileo Galilei and Sir Isaac Newton, we gained a precise understanding of force.
Galileo continued the ideas of medieval scholars and refuted Aristotelian ideas. He introduced the concept of inertia. He observed that objects in motion tend to stay in motion unless acted upon by an external force. However, he did not delve into the underlying reasons for this behaviour.
Later on, it was Sir Isaac Newton who built his elucidation upon Galileo’s work and provided a more comprehensive explanation of inertia. His work laid the groundwork for Newton’s laws of motion. His ideas provided a comprehensive framework and the mathematical formulation of force.
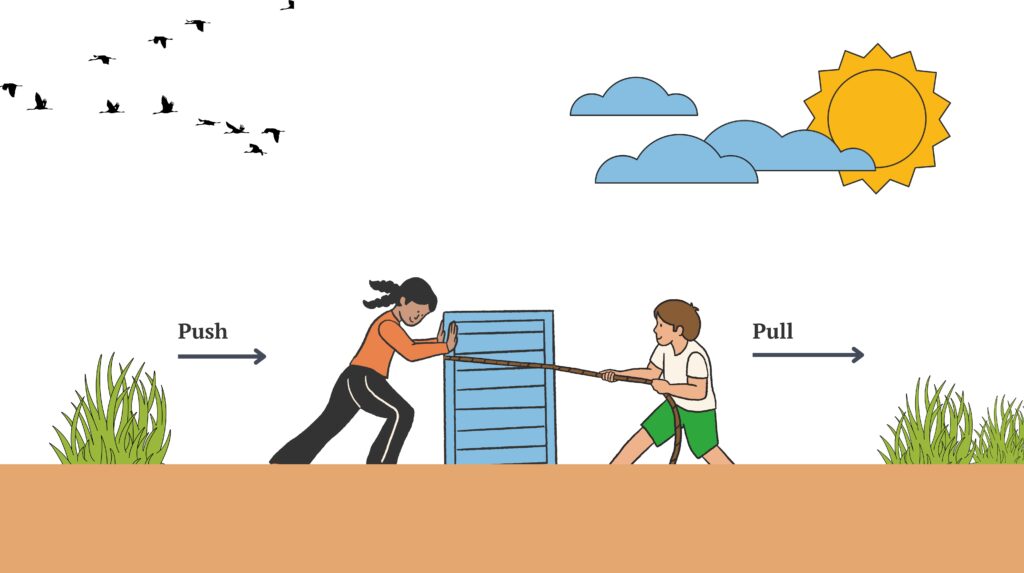
What is Force?
It is defined as,
“the push or pull on an object due to its interaction with another object is called a force.”
Key Characteristics of Force
Representation
Force is universally represented by the symbol ![]() .
.
Unit
In the International System of Units (SI), it is measured in newton (N).
Type of Quantity
Force is a derived quantity, as it depends on base quantities like mass and acceleration.
Nature of Quantity
Force is a vector quantity, meaning it has both magnitude and direction.
Mathematical Formulation
Mathematically it is represented by,
![]()
Where,
 = force,
= force, = mass of the object
= mass of the object = acceleration
= acceleration
What is Newton?
One Newton is the force required to accelerate a mass of one kilogram at a rate of one meter per second squared. It is given as,
![]()
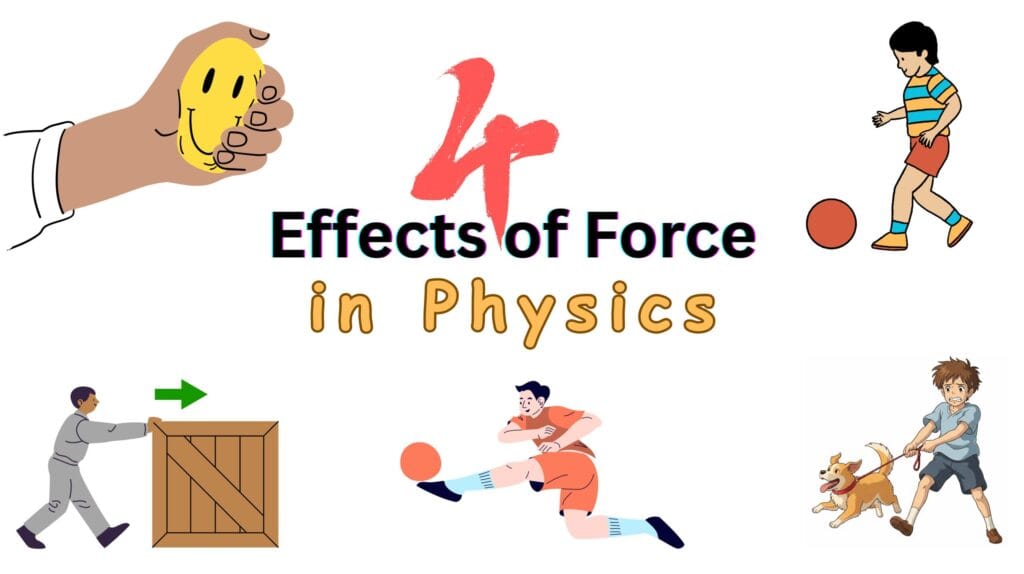
4 Effects of Force
Force can produce the following effects:
1. Change in Shape of an Object (Deformation)
It can change the shape of a body either by breaking or deforming it. For instance, stretching a rubber band or squeezing a softball in your hand.
2. Start or Accelerate an Object
It can initiate the motion of a body or increase the speed of a moving body. For instance, pushing a wooden box or an accelerating car or a track.
3. Change in Direction
It can change the direction of motion of a body. For instance, a player hitting a ball and changing its actual direction of motion.
4. Stop or Decelerate an Object
It can bring a moving body to rest or decrease the speed of a moving body. For instance, applying brakes to stop a vehicle or pulling your energetic dog back.
Examples
- A stationary book on a table remains at rest until pushed.
- A rolling ball continues to move until friction or another force slows it down.
Application of Force
It is integral to countless applications in daily life and technology:
- Sports: Athletes apply force to achieve desired motions.
- Transportation: Engines generate force to move vehicles.
- Construction: Forces are analysed to ensure structural integrity.
- Space Exploration: Rocket thrust overcomes gravitational force to propel spacecraft.
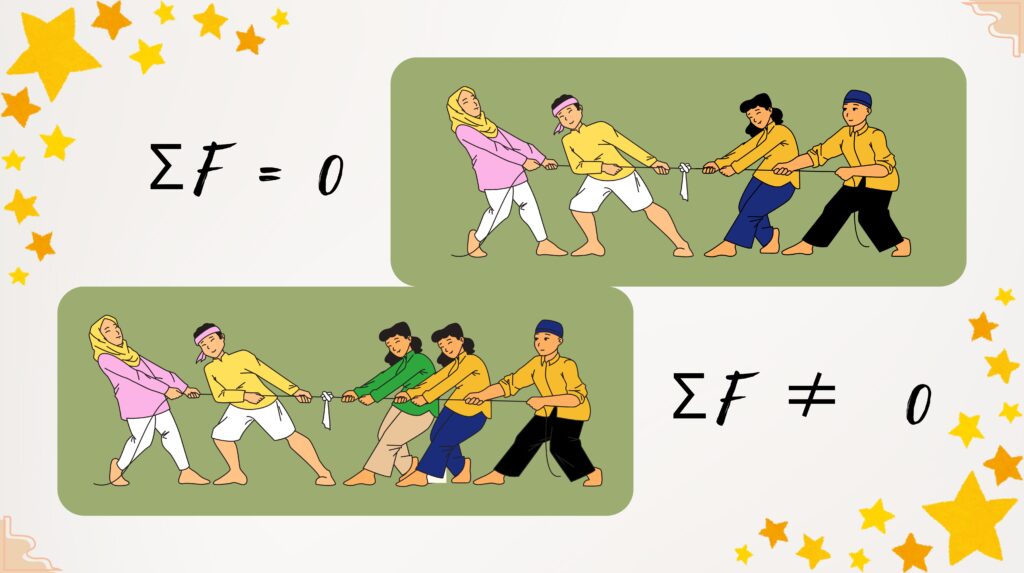
Net Force
The net force is the vector sum of all forces acting on an object. If it is zero, the object remains in its current state of motion. If it is non-zero it can move in either direction.
Inertia
Inertia is the resistance of an object to changes in its state of motion or rest. The greater the mass, the greater the inertia.
The Idea of Inertia
The idea of inertia was introduced by Galileo. He stated that an object in motion stays in motion unless acted upon by an external force.
Newton formalised this concept as the First Law ofMotion, also known as the Law of Inertia.
Law of Inertia
The law of inertia states:
“An object will remain at rest or move in a straight line at a constant velocity unless acted upon by an external force.”
Conclusion
Force is a cornerstone of physics, governing motion and interaction in every aspect of the universe. From its historical understanding to its modern applications, it continues to be an essential tool for interpreting natural phenomena.
By gaining a clear understanding of the its (forces) principles, humanity has unlocked the secret of technology. It not only shaped our world but also confirmed its significance in science and everyday life.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
What is Force in Physics and Its 4 Effects?
It is a push or pull that causes an object to move or change its motion. A force can:
- Deform a body.
- Change direction of a body.
- Start or accelerate a body.
- Stop or decelrate a body.
What are the types of forces?
They can be contact forces (like friction) or non-contact forces (like gravity).
What are Newton’s laws of motion?
They describe the relationship between force, mass, and acceleration.
What is the unit of force?
It is measured in Newtons (N).
What is inertia?
Inertia is the resistance of an object to changes in its state of motion.
What is the net force?
It is the vector sum of all forces acting on an object.
How does the force affect motion?
It can change an object’s speed, direction, or shape.
What is gravitational force?
It is an attractive agent that exists between masses.
What is a balanced force?
Balanced forces result in no change in motion.
Why is force important in physics?
It explains the interactions and movements of objects in the universe.

