Understanding motion and its types is fundamental in physics. From how a car moves on the road to the way planets orbit the sun, everything is about motion.
Table of Contents
Introduction
From the simplest rolling of a ball on the ground to the majestic orbiting planets around the sun, motion or movement is at the heart of everything we experience. Without it, life would stand still.
But what makes things move, and why do they behave the way they do? In order to understand this, we need to take a closer look at its key types in a way that makes even complex ideas easy to grasp.
Kinematics
It is defined as,
“the branch of physics that deals with the study of motion without the influence of force.”
It focuses on describing how objects move, but it does not consider the forces that cause the motion. It helps us analyse distance, displacement, speed, velocity, acceleration, and time.
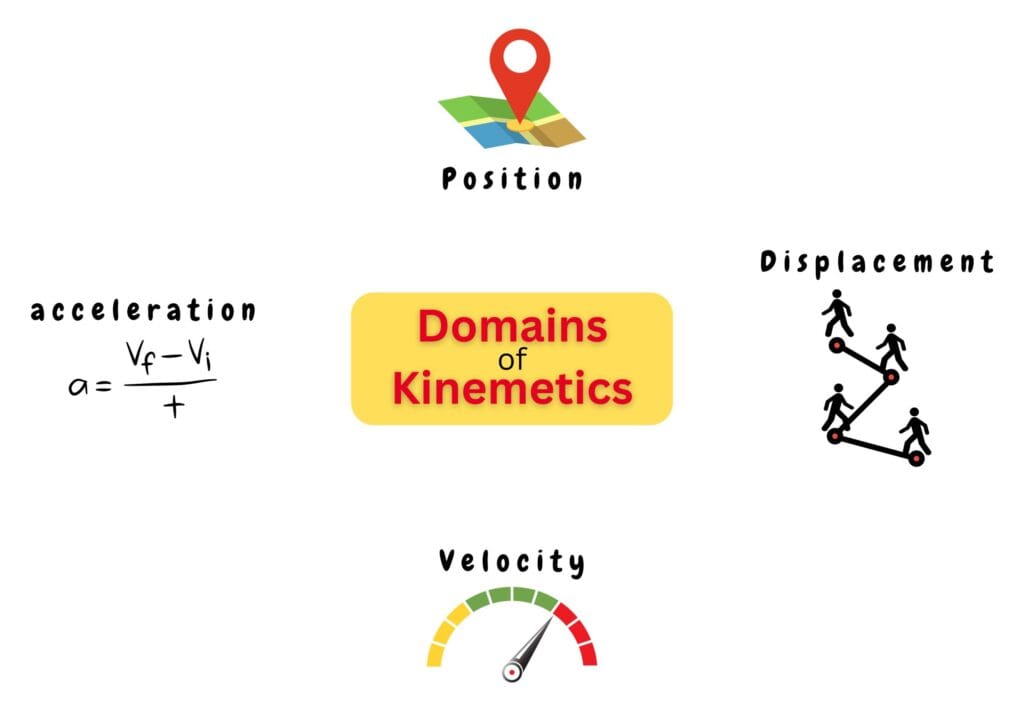
Domains of Kinematics
- Position: Where an object is located.
- Displacement: How far an object has gone in a given time.
- Velocity: How fast an object is moving and in which direction.
- Acceleration: How quickly velocity of an object changes over time.
Rest
When an object does not change its position over time, in a given frame of reference, it is said to be at rest.
Examples of Rest
- A book lying on a table.
- A chair in a room.
- A car in a garage.


Motion
When an object changes its position over time, in a given frame of reference, it is said to be in motion.
Motion can be fast or slow, depending on how quickly the object moves.
Examples of Motion
- A plane flying in the sky.
- A ball rolling on the ground.
- A person walking down the street.
Difference between Rest and Motion

Motion and Its Types
Motion appears in different forms. It depends on how objects move. There are 3 types of motion and are given below.
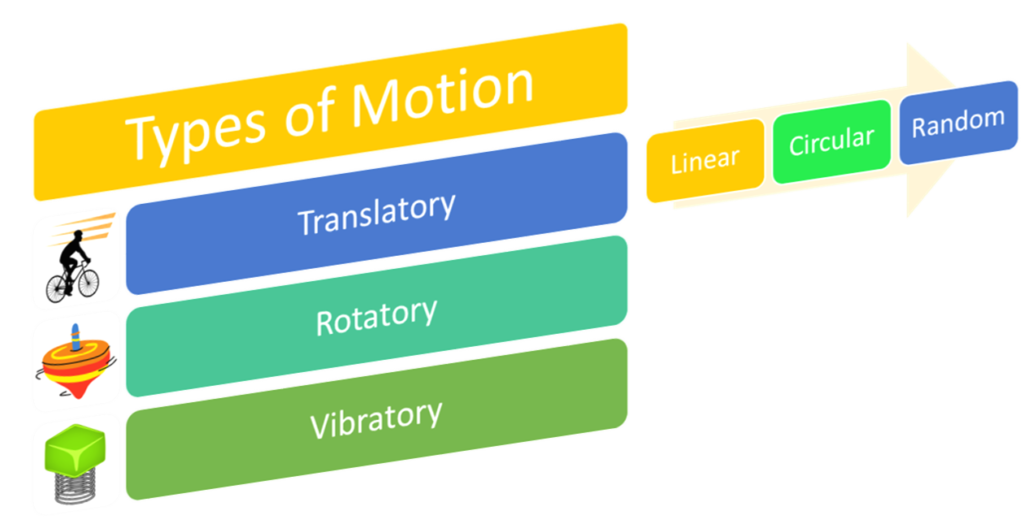
Translatory Motion
It is a type of motion in which all parts of an object move in the same direction and cover the same distance.
Types of Translatory Motion
This motion can be linear, circular, or random.
Linear Motion
It is the type of translational motion in which the object moves in a straight line.
Examples of Linear Motion
- A car moving on a straight road.
- A person running on a track.
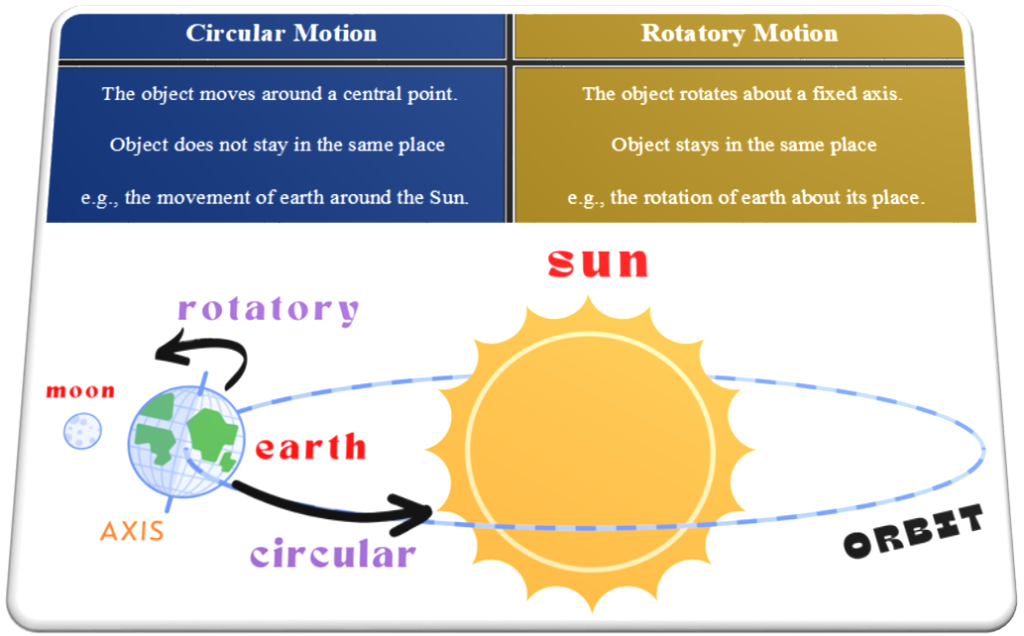
Circular Motion
It is the type of translational motion in which the object moves along a circular path.
Examples of Circular Motion
- The Earth orbiting around the Sun.
- Blades of a rotating fan.
Random Motion
It is the type of translational motion in which the object has no definite path.
Examples of Random Motion
- Movement of gas molecules.
- A butterfly flying in a garden.
Rotatory Motion
It is a type of motion in which an object rotates around a fixed axis.
The object stays in the same place while rotating.
Examples of Rotatory Motion
- A spinning top.
- A rotating wheel.
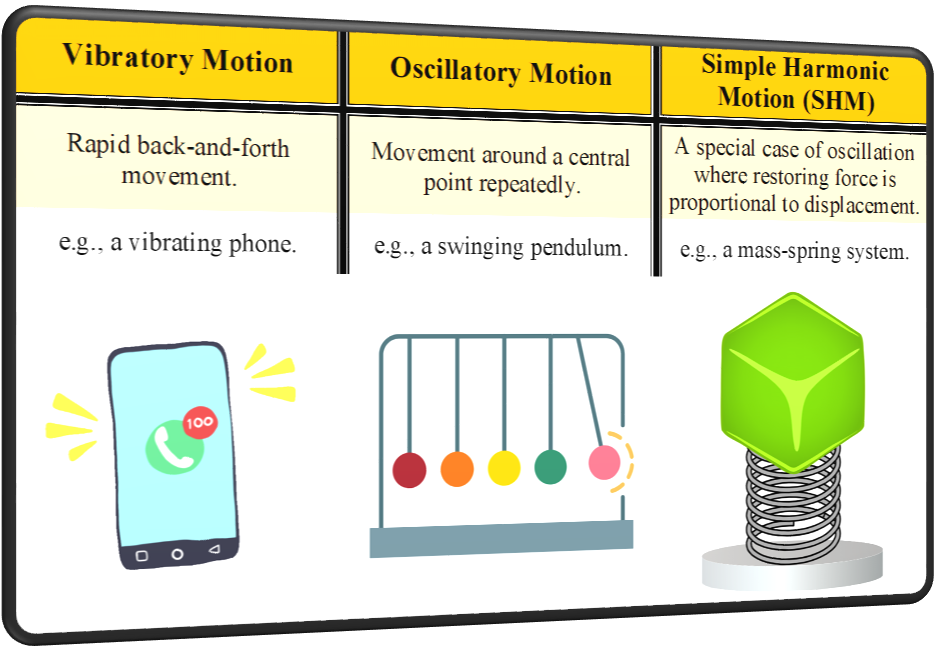
Vibratory Motion
It is a type of motion in which an object shows rapid back-and-forth movement.
Examples of Vibratory Motion
- The movement of a swing.
- A vibrating mobile phone.
Difference between Circular Motion and Rotatory Motion
Difference between Vibratory, Oscillatory, and Simple Harmonic Motion (SHM)
Uniform Motion vs Non-Uniform Motion
Uniform Motion
When an object covers equal distances in equal intervals of time, regardless of how small those intervals are, it is said to be in uniform motion.
Non-Uniform Motion
When an object covers unequal distances in equal intervals of time or equal interval of distances in unequal interval of time, it is said to be in non-uniform motion.
Conclusion
Understanding motion and its types is key to exploring the world of physics. It governs much of what we observe in everyday life. From the way planets move to the vibrations in sound, every seen and unseen able either in the state of motion or at rest.
Whether it is the straightforward linear motion or the complex vibratory motion, everything moves, and now we know how!
Frequently Asked Question (FAQs)
What is motion in physics?
Motion refers to the change in position of an object over time in a given frame of reference. It can be slow or fast, depending on how quickly the object moves.
What are the three main types of motion?
The three main types of motion are translatory motion, rotatory motion, and vibratory motion.
What is kinematics?
Kinematics is the branch of physics that studies motion without considering the forces that cause it. It focuses on concepts such as displacement, velocity, and acceleration.
What is the difference between rest and motion?
An object is at rest when it does not change its position over time, while an object in motion changes its position with time in a given frame of reference.
What is translatory motion?
Translatory motion is a type of motion in which all parts of an object move in the same direction and cover the same distance. It can be linear, circular, or random.
What is the difference between linear and random motion?
In the former, the body follows a definite path, like a moving car. However, in the later, the body does not follow a definite path, like a butterfly.
What is the difference between circular motion and rotatory motion?
Circular motion involves an object moving along a circular path, while rotatory motion involves an object rotating around a fixed axis without changing its location.
What is vibratory motion?
Vibratory motion is a type of motion where an object moves rapidly back and forth. Examples include a vibrating mobile phone and the movement of a swing.
Name a situation when a body is at rest and in the motion at the same time?
A person sitting in a vehicle, moving with uniform speed, is both at rest and in the motion.
Why is understanding motion important in physics?
Understanding motion is fundamental to physics as it helps explain how objects move, whether in straight lines, along curves, or vibrating back and forth. Motion governs much of the physical world, from planets orbiting the sun to everyday objects.
