In our lives, there are vast applications of Newtons 3 Laws of Motion, and we see them in action in various places, assisting us and making our lives easier.
Table of Contents
Introduction
The understanding of force dates back to Aristotle, a Greek philosopher, who proposed early theories about motion. However, it was Sir Isaac Newton–one of the most brilliant minds in history, during the Classical Period, who clarified these concepts with his ground-breaking work.
He revolutionised our understanding of motion and mechanics. His “Philosophiæ Naturalis Principia Mathematica” (1687) introduced the Three Laws of Motion. These laws of motion formed the foundation of classical mechanics.
Significance of Newtons 3 Laws of Motion
These laws are essential for understanding how objects move and interact in our universe. To learn about these laws of motion in depth, we will see some relatable examples and real-world applications.
Newton’s 1st Law of Motion (The Law of Inertia)
The first law of motion states that:
“An object will remain at rest or in uniform motion in a straight line unless acted upon by an external force.”
Significance of the Law
The 1st law of motion emphasises the concept of inertia, which is the tendency of an object to resist changes to its state of motion. That is why, this law is also known as The Law of Inertia.
In simple terms, a stationary object will not move unless a force is applied, and a moving object will not stop or change direction until an external force is applied.
Examples
1. A Book on a Table
The book stays stationary because no external force is acting on it to move it. However, if we push the book, our applied force overcomes inertia and sets it in motion.

2. A Car Abruptly Stopping
When the brakes are applied, passengers lurch forward because their bodies tend to remain in motion, even though the car has stopped.
Applications
Seatbelts in vehicles are a good application to understand the law of inertia (or the 1st law of motion). When the brakes are applied, the seatbelts counteract inertia during sudden stops. Thus, it prevents passengers from continuing forward and reducing injury risks.
Newton’s 2nd Law of Motion (The Law of Force and Acceleration)
The 2nd law of motion states that:
“The force acting on an object is equal to the mass of the object multiplied by its acceleration (F = ma).”
OR
“The acceleration of an object is directly related to the applied force on the object and inversely related to the mass of the object.”
Mathematical Formulation
According to the statement of Newton’s 2nd law:
![]()
![]()
Combining both proportionalities:
![]()
![]()
![]()
For a body of mass ![]() , moving with an acceleration of
, moving with an acceleration of ![]() , and experiencing a net force of
, and experiencing a net force of ![]() , the value of
, the value of ![]() is:
is:
![]()
![]()
Replacing back the value of constant, we get:
![]()
![]()
OR
![]()
Significance of the Law
The 2nd law of motion quantified the force for the first time. It establishes the relationship between the force (F), mass (m), and acceleration (a).
The law describes how the motion of an object changes when subjected to an external force. The greater the force, the greater the acceleration, but for a given force, an object with a larger mass will accelerate less.
Examples
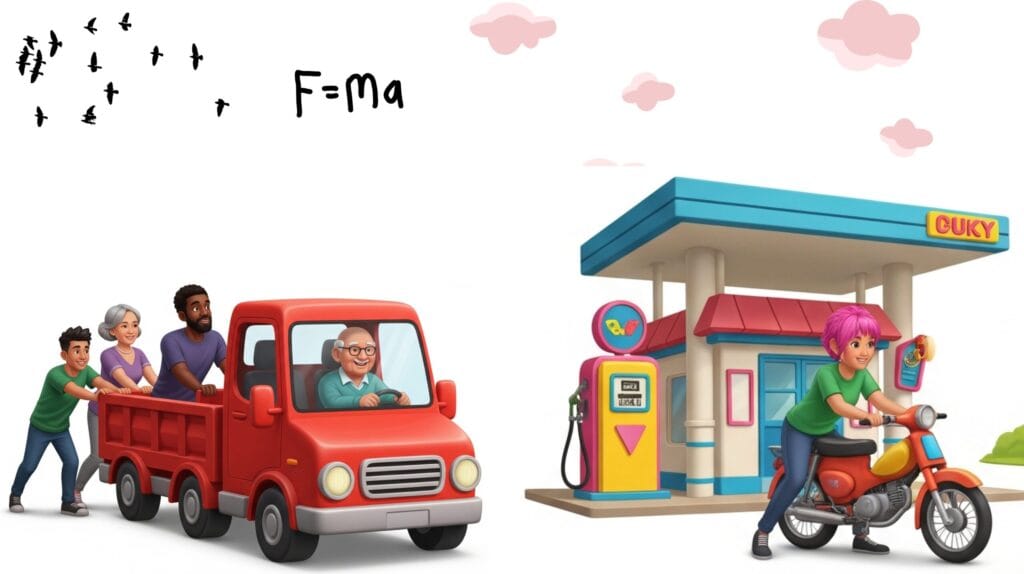
1. Pushing a Motor Bike vs a Truck
A motorbike is easier to push (more acceleration or ![]() ) as compared to a truck (less acceleration or
) as compared to a truck (less acceleration or ![]() ).
).

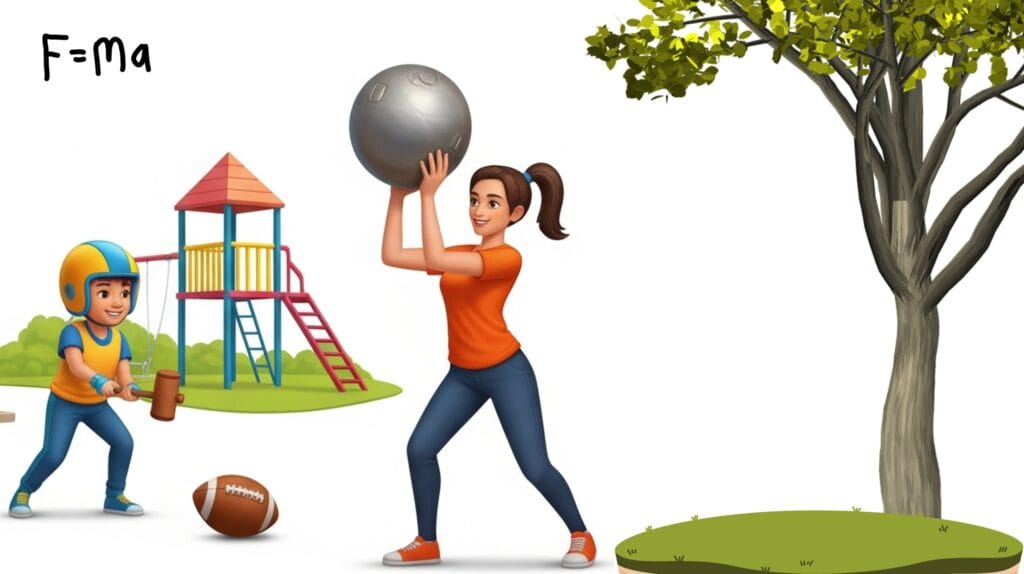
2. Throwing a Metallic Ball vs a Tennis Ball
A tennis ball (lesser mass) is easier to throw – more ![]() – than a metallic ball (heavier mass) – lesser
– than a metallic ball (heavier mass) – lesser ![]() .
.

Applications
The journey of a rocket gives us a good understanding of the relationship between force, mass, and acceleration. The force generated by a rocket, by burning the fuel, overcomes the gravity of Earth to propel it into space.
Newton’s 3rd Law of Motion (The Law of Action and Reaction)
The 3rd law of motion states that:
“For every action, there is an equal and opposite reaction.”
OR
“Every action has a reaction which is equal in magnitude but opposite in direction.”
Significance of the Law
This law highlights the mutual interactions between two objects. When one object exerts a force on another, the second object exerts an equal and opposite force back on the first.
Examples
1. Walking on the Ground
When we walk, we push the ground with our feet in the backward direction. As a reaction, the ground propels us forward with an equal and opposite force.
A Rocket Launch
The fascinating scene of a rocket launch is an example application of 3rd law of motion. The exhaust gases from the engine of a rocket move downward with great force. As a reaction, the gases push the rocket upward with an equal and opposite force.
Applications
We can navigate through the air, land, or water, or even in space via airplanes, cars, ships, rockets, and space shuttles, respectively. All these modes of transportation would have not been possible without the refined and comprehensive idea of the 3rd law of motion.
Conclusion
Newton’s 3 Laws of Motion provide a universal framework for understanding the mechanics of the physical world. They bridge the gap between theoretical physics and practical applications. It has enabled us to develop technologies that shape our lives.
By exploring these laws of motion, we not only appreciate the elegance of Newton’s insights but also gain a deeper understanding of the forces governing the universe.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
What are Newton’s 3 Laws of Motion?
Newton’s 3 Laws of Motion are foundational principles in physics that describe the relationship between forces and motion. They include the Law of Inertia, the Law of Force and Acceleration, and the Law of Action and Reaction.
Why are Newton’s 3 Laws of Motion important?
These laws provide the basis for understanding motion and interactions in our universe. They are essential in fields like engineering, transportation, and space exploration.
What is the significance of the 1st Law of Motion?
The 1st Law, also known as the Law of Inertia, explains that objects remain at rest or in uniform motion unless acted upon by an external force.
What does Newton’s 2nd Law of Motion state?
It states that the force acting on an object is equal to the mass of the object multiplied by its acceleration (F = ma). It quantifies the relationship between force, mass, and acceleration.
How does the 3rd Law of Motion apply to real life?
The 3rd Law states that for every action, there is an equal and opposite reaction. Examples include rocket propulsion, walking, and swimming.
What is an example of the 1st Law of Motion?
A book resting on a table remains stationary unless you push it, demonstrating the concept of inertia.
How is Newton’s 2nd Law applied in daily life?
Pushing a lighter object, like a tennis ball, is easier than pushing a heavier object, like a metal ball, because the lighter object accelerates more with the same force.
What role does Newton’s 3rd Law play in transportation?
Vehicles like airplanes and rockets use the 3rd Law to generate motion, with engines producing thrust by expelling gases or air in the opposite direction.
What is the connection between Newton’s Laws and space exploration?
Newton’s Laws govern spacecraft trajectories, rocket launches, and orbital mechanics, enabling precise calculations for space missions.
How do Newton’s Laws influence engineering and construction?
Engineers use these laws to design stable structures and reliable machinery, ensuring they can withstand forces and maintain efficiency.

