What is couple in physics? It is a fascinating concept in mechanics–a branch of physics, in particular engineering– and holds great significance in understanding rotational motion and the mechanics of rigid bodies.
Table of Contents
Introduction
In physics, the concept of a couple is pivotal for understanding rotational motion. It causes an object to rotate without any translational motion. This is one of the fundamental phenomena in the field of mechanics. It is observed in various everyday activities and engineering applications.
What is a Couple?
In physics, a couple is defined as,
“a pair of equal and opposite forces with non-coincident points acting on a body, causing the rotational or turning effect.”
These forces do not share the same line of action. As a result, they cause a rotational effect without producing any linear motion. In essence, it is a combined effect of two turning or twisting actions in the same direction and, is pivotal in various mechanical systems.
It is also called the moment of a couple (MoC).
Key Properties of Couple
Both torque and moment–which are the turning effects of forces–share the key properties with the MoC (represented either as ![]() or
or ![]() ).
).
How Does a Couple Work?
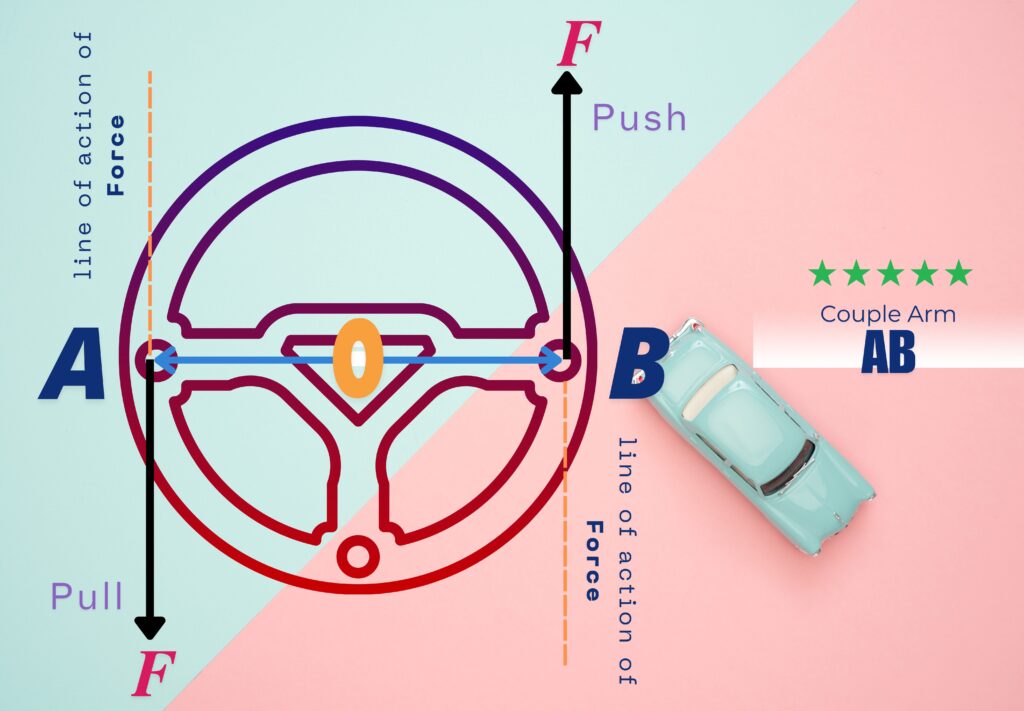
To understand how a couple works, imagine turning a steering wheel. When we apply force on the wheel with both hands, one hand pushes forward, and the other pulls backward. These forces form a couple, causing the wheel to rotate.
Mathematical Formulation
The turning effect of a MoC is quantifiable. To know how the it is calculated mathematically, consider a steering wheel as shown above.
As clear from the figure,
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
Effectiveness of Couple
Its effectiveness depends on two main factors,
- Magnitude of the Forces
- Perpendicular Distance Between the Forces (also known as the “couple arm”)
Key Characteristics of a Couple
A list of its key characteristics are given here.
1. Equal Forces
The two forces involved in MoC are of the same magnitude.
2. Unlike Forces
These forces act in opposite directions and produce a turning effect.
3. Different Lines of Action
The lines of action of these forces are parallel but not coincidental.
4. Purely Rotational Effect
MoC produces only rotation, with no net translational motion.
Couples in Everyday Life
Some examples from everyday life regarding the MoC are listed here.
1. Winding a Clock
Turning the key to wind the clock involves a couple.
2. Unlocking a Key Lock
Insert a key into the lock hole and then rotate with a finger and a thumb (MoC) to open the lock.
3. Using a Wrench
Applying force on a wrench to tighten or loosen a bolt, the MoC helps in achieving the desired rotation.
4. Opening a Jar Lid
Twisting the lid involves applying equal and opposite forces with your hands, creating MoC that rotates the lid.
Applications of Couples in Engineering and Technology
It plays a critical role in engineering and mechanical systems. Some key applications include:
- Automobiles: The steering mechanism, braking systems, and even the operation of engines involve MoC.
- Machinery: Industrial machines often rely on MoC for torque and rotational motion.
- Aerodynamics: MoC are crucial in controlling the pitch, yaw, and roll of airplanes.
- Robotics: Robots use MoC for precise rotational movements in their joints.
Why is the Concept of “Couple” Important?
Understanding this concept is essential because it,
- Provide insights into rotational motion and stability.
- Help in analysing and designing mechanical systems.
- Play a vital role in balancing forces in static and dynamic systems.
Common Misconceptions about MoC
There are some misconceptions that circle around it.
- MoC Depend on the Point of Application: Not true. The moment of a MoC is independent of the reference point.
- MoC Cause Linear Motion: False! MoC only induce rotation and have no net effect on the linear motion of a body.
- Any Two Forces Form a MoC: Incorrect. The forces must be equal in magnitude, opposite in direction, and have different lines of action to constitute a MoC.
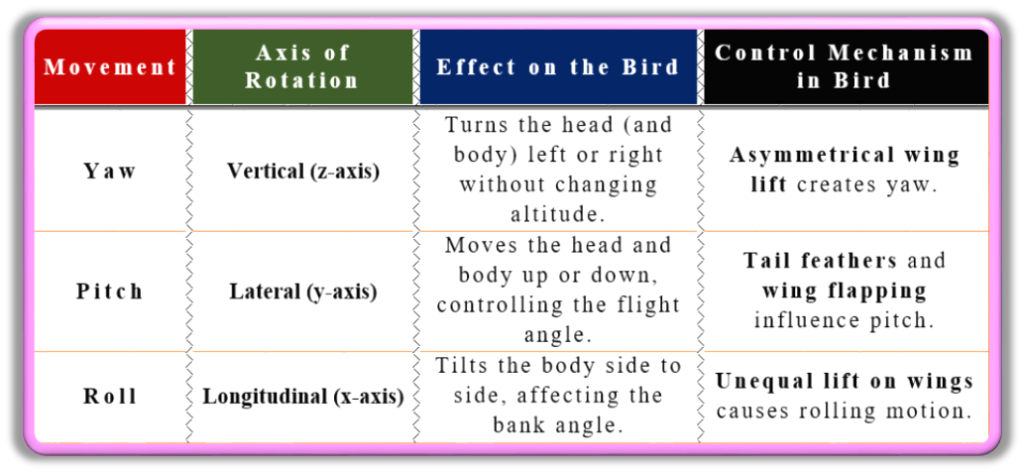
MoC in Nature
Nature also demonstrates the concept of MoC. For instance, when birds flap their wings, the forces generated can form MoC, aiding in their rotational and linear movements. Here is the summary for that:
Conclusion
The concept of MoC in physics is simple yet profound. It helps us understand how rotational forces operate in various systems, from everyday tools to complex machinery. By grasping the fundamentals of MoC, we can better appreciate the elegance of mechanics and its applications in real-world scenarios.
Next time you twist a jar lid or steer a car, remember—you are applying the concept of MoC in action! Physics is truly everywhere, making our lives easier and more dynamic.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
What is couple in physics?
It is a pair of equal and opposite forces with non-coincident lines of action, causing a purely rotational effect on a body.
How is MoC different from a single force?
A single force can cause both linear and rotational motion, whereas a couple causes only rotational motion without any translational effect.
What is the formula for calculating the moment of MoC?
The MoC is calculated as:
![]()
Here, ![]() is the magnitude of the force, and
is the magnitude of the force, and ![]() is the perpendicular distance between the forces.
is the perpendicular distance between the forces.
Can MoC exist if the forces are not equal?
No, for a MoC to exist, the forces must be equal in magnitude, opposite in direction, and have different lines of action.
What is the role of MoC in steering a car?
In steering, MoC is created by applying force with both hands in opposite directions, causing the wheel to rotate.
Does MoC depend on the reference point?
No, the MoC is independent of the reference point.
What are the key characteristics of MoC?
- Equal magnitude of forces
- Opposite directions of forces
- Parallel but non-coincident lines of action
- Produces only rotational motion
Can a MoC cause linear motion?
No, MoC induces only rotational motion and does not produce any net linear motion.
What are some practical examples of MoC in everyday life?
- Turning the steering wheel
- Opening a jar lid
- Using a wrench to tighten or loosen a bolt
Why is understanding the concept of MoC important in engineering?
It helps in designing mechanical systems, ensuring stability, and analysing rotational motion in machinery, vehicles, and robotic systems.
